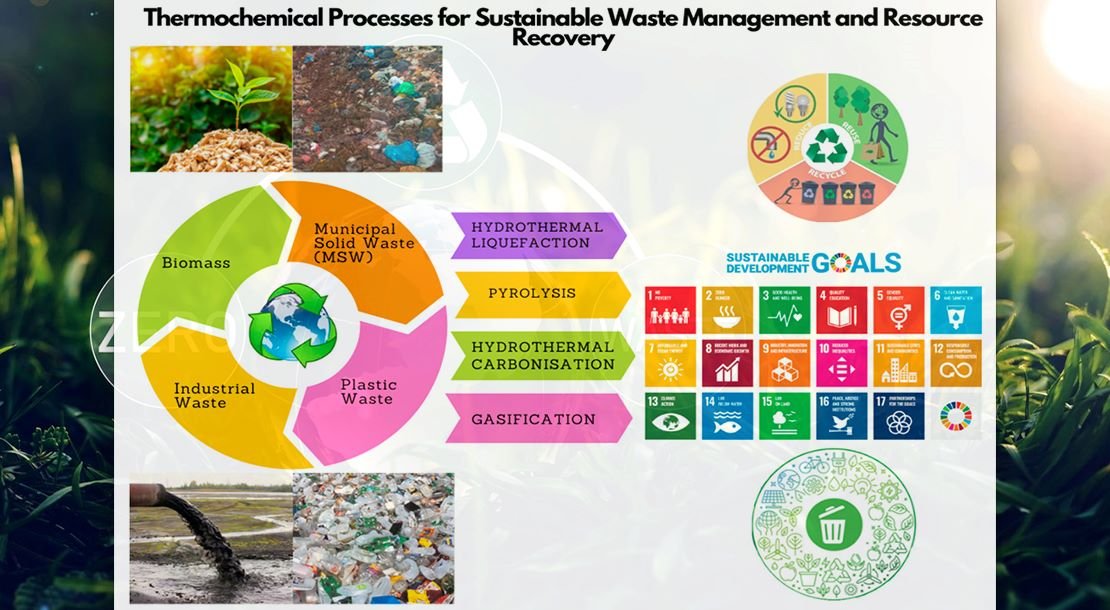
In recent years, Indian corporations have significantly elevated their commitment to environmental sustainability through Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives. With the Companies Act, 2013 mandating CSR spending, many organizations have gone beyond compliance to embed sustainability into their core strategies. This report examines the environmental CSR efforts of some of India’s most influential companies, highlighting their innovative approaches and measurable impact.
Tata Group has long been a pioneer in CSR, and its environmental initiatives continue to set benchmarks. Tata Steel’s flagship programs focus on water conservation, afforestation, and waste management. The company has implemented large-scale rainwater harvesting systems and aims to achieve zero effluent discharge across its operations. Tata Power, through its “Act for Mahseer” campaign, has also contributed to aquatic biodiversity conservation, while Tata Green Energy is investing heavily in solar and wind energy to reduce carbon emissions.
Wipro Limited has adopted a holistic approach to sustainability. Its “Earthian” program engages students and educators in environmental education, while its internal operations emphasize renewable energy, water recycling, and zero-waste-to-landfill policies. Wipro’s green buildings and closed-loop waste management systems have significantly reduced its ecological footprint.
Infosys has emerged as a leader in green innovation. The company has committed to becoming carbon neutral and has invested in energy-efficient campuses, solar power installations, and afforestation projects. Infosys has also published detailed sustainability reports aligned with global frameworks, reinforcing transparency and accountability.
Reliance Industries, through the Reliance Foundation, has launched several impactful environmental programs. These include mangrove restoration, climate-resilient agriculture, and clean energy adoption in rural areas. The foundation’s “Bharat India Jodo” initiative integrates environmental sustainability with rural development, promoting long-term ecological balance.
Vedanta Group has pledged $5 billion to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. Its CSR programs focus on renewable energy, biodiversity protection, and waste management. Notably, Vedanta has partnered with the World Economic Forum’s 1t.org initiative, committing to plant 7 million trees. The company’s solar and water conservation projects have benefited millions across India.
Hindustan Unilever (HUL) has aligned its CSR with the “Unilever Compass” strategy, focusing on sustainable living. HUL’s “Swachh Aadat, Swachh Bharat” campaign promotes hygiene and environmental awareness, while its sustainable farming initiatives support local ecosystems and reduce chemical usage.
ITC Limited has integrated environmental goals into its business model through afforestation, watershed development, and sustainable agriculture. Its “e-Choupal” platform empowers farmers with eco-friendly practices, while its large-scale tree plantation drives contribute to carbon sequestration and biodiversity conservation.
These initiatives reflect a broader shift in Indian corporate culture—from reactive compliance to proactive environmental leadership. As climate change intensifies, such CSR efforts not only mitigate ecological risks but also enhance brand equity, stakeholder trust, and long-term resilience.